SEO: A Jungle survival guide
What is SEO?
Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) is the process by which you make your website easier for searchers to find, by using online marketing techniques to get it ranked more highly by search engines such as Google, Bing and Yahoo! Research has shown that internet users trust organic search results far more than paid for ads so most website owners work hard to be ranked highly, organically.
Basically, SEO takes into consideration a number of factors: how search engines work; what people search for; the keywords and terms used; and search engine preference by target audience.
Optimising a website is a specialist job best undertaken by an Internet marketing agency. It involves the detailed analysis of search data and the performance of individual pages of your website. This information then informs a strategy to edit the content of the site eg adding more occurrences of certain keywords, adding new pages, tweaking meta data etc. Another SEO Internet marketing strategy is to increase the number of backlinks, (also known as inbound links) from other reputable websites.
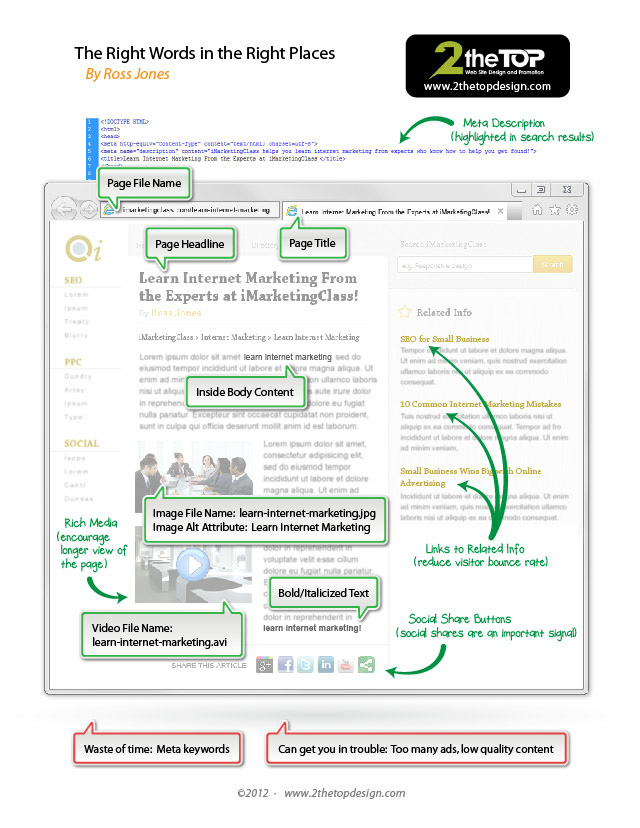
What is meta data? Below is an infographic, courtesy of topdesign.com, which explains the different types of meta data on a webpage.
Market size/Industry trends
Twelve years ago, SEO was a rare and misunderstood discipline, often described as a ‘dark art’. There was a lot of poor practice, as is typical with emerging technologies, which tarnished the reputation of the industry as a whole.
Fast forward to 2010, and the SEO market in the UK grew by a massive 16% to £436m. The growing importance of the discipline was underlined by an eConsultancy survey which found that 93% of digital marketers expect to increase their SEO budget by more than 20% in the next 12 months.
Today, unethical techniques that are penalised by search engines have largely disappeared as the industry has grown up, and marketers understand the central role that SEO needs to play in their digital strategies. With 49% of UK eCommerce companies reporting their ROI from SEO has increased in the last 12 months, there’s little doubt SEO is here to stay.
Advantages of SEO
SEO is often the digital marketing strategy of choice because organic search is perceived to be more cost-effective in comparison to paid search or online display advertising. However, to be done well, it requires ongoing commitment and time.
Search Engine Optimisation allows for national and global reach and is considered to be an unsurpassed method of driving targeted, qualified traffic to your site, the volumes of which can be easily predicted and measured.
SEO allows challenger brands to compete with the big boys in the digital habitat and is now an established and reputable method for building brand awareness – although preferably as part of a wider integrated digital campaign.
Disadvantages of SEO
Although organic search is free (ie you don’t pay for clicks) you’ll need to invest in other areas to ensure you get to the top of the search engine rankings. These typically include website improvements, content and copywriting, link-building and PR.
In addition to identifying keywords and phrases, search engines now take into account over 200 different criteria when judging how to rank your website – so SEO isn’t something you should consider managing on your own.
At Jungle, we see more and more weight being given to things like site design and navigation, the frequency at which the site is updated and the amount the site is shared on social media networks, but the importance placed on individual factors changes weekly.
The infographic below, courtesy of searchengineland.com, is a snapshot explaining the comparative weightings given to different factors at a given time.
Glossary
We thought this bite-sized glossary of keywords and phrases might prove useful.
- Algorithm:
- A step-by-step operational programming rule for calculations to determine how a search engine indexes content and displays the results to its users.
- Black Hat SEO:
- Sometimes referred to as spamdexing, this is the use of any unethical and unprofessional optimisation tactics that cause a site to rank more highly than its content would otherwise justify. This process is against search engine guidelines and could result in a site being penalised or even removed from the index.
- Backlinks:
- A hyperlink on another website that leads to your website. Also known as incoming links or inbound links.
- HTML:
- An acronym for Hyper Text Markup Language – programming code used to mark up web content and display it in a formatted manner.
- H1 Tag:
- This is an Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML) tag often used to indicate a website page or section heading and paid special attention to by search engines.
- IP Address:
- Internet Protocol Address, sometimes also referred to as IP or Internet Address, is a series of numbers that identifies each server or device connected to the Internet.
- Javascript:
- A programming language run on the Internet user’s computer rather than the web server’s computer and works on all major browsers, such as Internet Explorer, Safari and Firefox.
- Keywords:
- The key search query typed into a search engine.
- Linkbait:
- Entertaining web content or feature designed to grab attention and compel others to link to it.
- Meta Data:
- A short description inserted into your website’s code that often appears along with your title tag in the search engine results.
- Meta Tags:
- Basically, hidden data that describes other data that is associated with a web page and placed in the HTML. Unfortunately these are overlooked by most major search engines.
- Organic or Natural Search Results:
- Listings on search engine results pages that appear as a result of their relevance to the search terms – ie not advertisements.
- Spam:
- Any manipulative techniques used to violate search engines including unsolicited bulk messages sent indiscriminately. Definitely not recommended or used by Jungle!
- Spider:
- Also known as a robots, bots or crawlers, spiders are programmes used by a search engine to explore the World Wide Web and locate pages for indexing.
- XML Sitemap:
- Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a sitemap scripting language that allows the programmer to list the content of a website for use by the search engine.
Useful Links
http://www.seomoz.org
http://searchengineland.com
http://www.mashable.com
http://www.sempo.org
http://searchenginewatch.com

